On a MacBook Pro 16-inch 2019 (Intel), under macOS Ventura 13.1, if
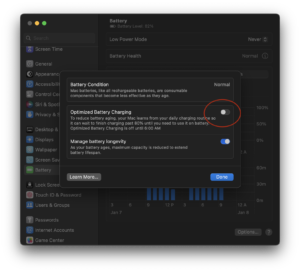
- the “Optimized Battery Charging” option is turned on in System Settings -> Battery
- the power adapter is plugged in
- the battery has charged to 80% or more under macOS
- the machine is then rebooted into Windows 10, using Boot Camp
- then: in Windows, the battery will not charge at all. Windows will report the battery as “Plugged in” but the battery will not charge. The battery will slowly drain to 0% as the machine is used.
Solution
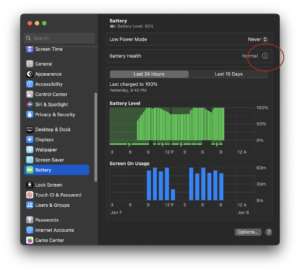
Disable Optimized Battery Charging temporarily or permanently before rebooting into Windows 10 under Boot Camp, in System Settings -> Battery -> Battery Health -> Info disclosure
Discussion
Optimized Battery Charging is a new feature introduced in recent macOS versions to preserve the health of Intel MacBook Pro batteries. It is known that if a laptop is not being used on battery, then it is best to charge to 80% instead of full. macOS purports to learn its user’s laptop battery usage patterns, and will charge the battery to 80% under normal adapter usage, and only begins charging to full when it expects the user to go to battery power soon.
However, it seems to do this by instructing some SMC/firmware level controller to stop charging the battery once current capacity hits 80% or more. When rebooted into Windows 10, which does not understand this optimized charging feature, there is no corresponding instruction to begin charging the battery again when the capacity falls below 80%. The consequence is that the laptop battery will steadily drain to 0%, and nothing will make it charge again until the machine is rebooted back into macOS.
This is an understandable edge case that Apple engineers didn’t test for. However, it seems to have started only recently (I don’t recall macOS Monterey having this behavior). Until it is fixed, if regular Windows 10 / Boot Camp usage is expected, it is best to leave the Optimized Battery Charging feature turned off on the macOS side — temporarily or permanently.
Worth noting that there are multiple other possible reasons that Windows 10 / Boot Camp is causing battery drain on a MacBook Pro. For example, the 16-inch 2019 MBP’s white 96W USB-C charger looks identical to the 87W USB-C charger from previous-gen MacBook Pro 15. If mistakenly or deliberately used to power the 16-inch MBP, then under full load the 87W adapter is insufficient to run the laptop. In this scenario the OS will tap the battery in complement with the adapter, causing a steady drain. Windows also runs more inefficiently than macOS on MacBook Pro, so under full CPU/GPU usage, it seems to take more power sometimes than even the 96W adapter can provide.
However, in either of those cases, the drain is very slow. In the case of the Optimized Battery Charging bug described above, under full CPU/GPU usage, the battery drains extremely quickly, with 30 minutes of usage causing 50% or more battery drain sometimes. This is because in this case, the laptop is not drawing power from the adapter at all.